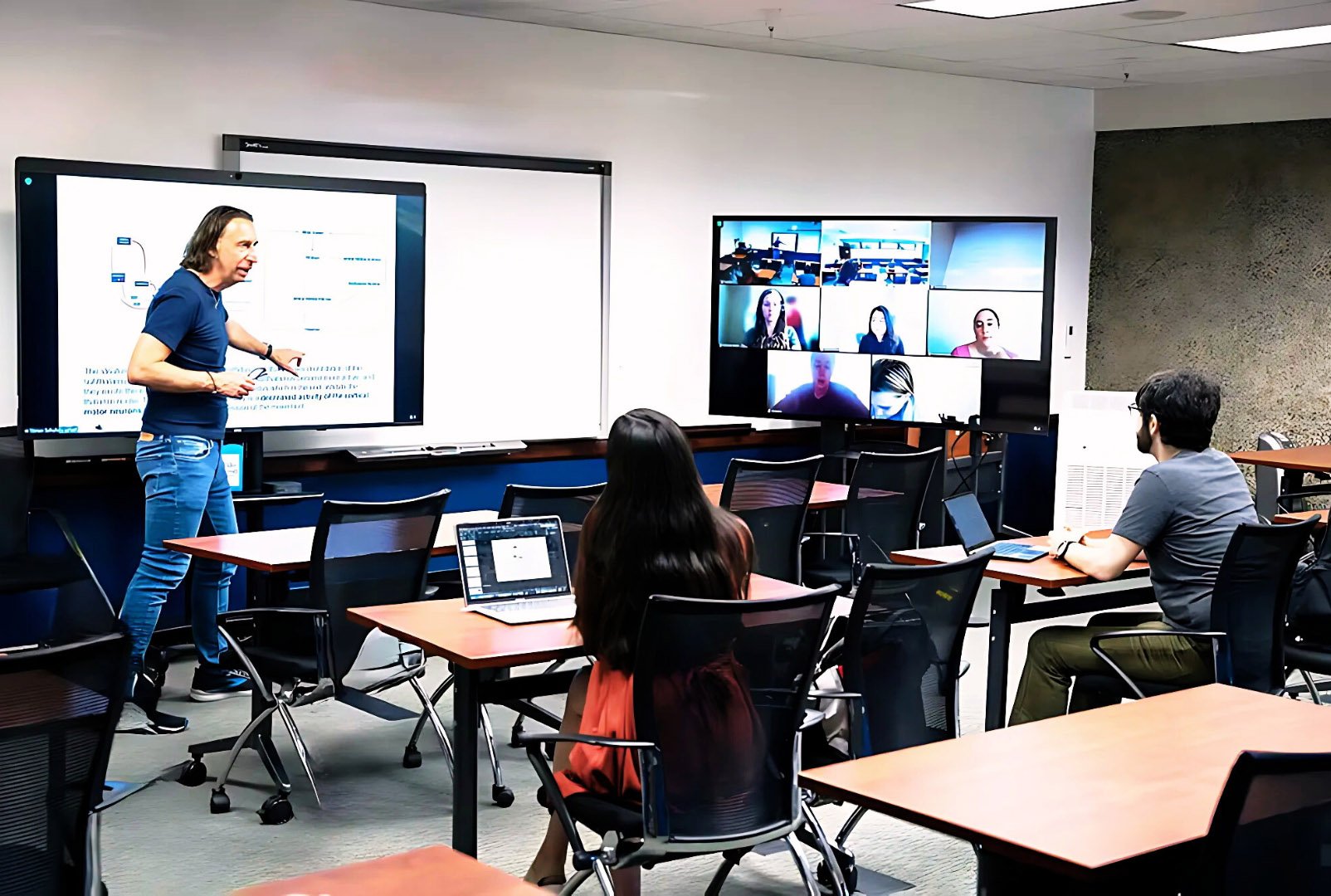
Master of Science in Psychology
Advance Your Career with Flexible, Online Learning in PAU’s MS in Psychology
The online Master of Science in Psychology degree at Palo Alto University empowers working professionals to pursue advanced leadership roles, effecting impactful change in mental health and beyond.
To create a flexible learning experience, Palo Alto University offers the Master’s program in a part-time, fully online format, with courses delivered in the evening. This commitment to flexibility allows most of our students to maintain full-time employment while enrolled in this rigorous graduate program.
Bachelor of Science in Psychology and Bachelor of Science in Business Psychology.
PAU offers two Bachelor of Science degrees tailored to launch your career in mental and behavioral health. The BS in Psychology prepares you for community advocacy, client support, and graduate study with flexible online classes and an optional internship. The BS in Business Psychology applies psychology to business fields like marketing and human resources, opening doors to careers and graduate programs.
Both degrees provide pathways to PAU’s advanced graduate degrees to help you grow professionally.

Reasons to Earn Your Master’s in Psychology at Palo Alto University
Through engaging coursework, research, and a supportive academic environment, graduate students earning their MS in psychology acquire in-demand skills, valuable insight into human behavior and mental processes, and professional development.
Request Information
Launch Your Future with Real-World Impact
89%
of MS in Psychology students are employed or continuing their studies upon graduation
.jpg?width=640&height=481&name=Cal-ex-Bal-W23-P0284-2160H%20(1).jpg)
Diverse Career Paths with an MS in Psychology: From Clinical to Tech Roles
Careers in Forensic Psychology
- Law Enforcement
- Corrections
- Legal Settings
- Education & Research
- Healthcare
- Non-Profits & Government Agencies
- Mental Health Start-up Companies
Careers in Technology & Mental Health
- Education & Research
- Media
- Healthcare
- Forensics
- Non-Profits & Government Agencies
- Business & Human Resources
- Mental Health Start-up Companies
- User Experience (UX) Design & Research
Program Highlights
Accessible Online Education
Specialized Concentrations
PhD Preparation Pathway

Who Should Apply?
- Career Changers: Transition into mental health and related fields, and make an impact.
- Mental Health Professionals: Specialize, advance your skills, or elevate your career.
- Working Professionals: Balance work and study with flexible, online, part-time options.
- Aspiring PhD Students and Master’s Candidates: Build a strong foundation for doctoral studies or an advanced graduate degree.
PhD Prep
Planning on pursuing a doctorate in psychology? Students working toward their MS in Psychology may apply to transition into the PAU residential PhD in Clinical Psychology program when entering the program's second year. The PhD Prep concentration is an effective way to demonstrate academic readiness for graduate-level work.
The PhD program is selective; students must meet academic qualifications to receive an invitation to interview. Admission to the PHD program is not guaranteed.
One-Week Residency
Students on the PhD Prep Concentration come to the Palo Alto campus for one week for an intensive course in Clinical Interviewing.
The forensic psychology concentration is an excellent educational track for graduate students interested in careers in the criminal justice or legal disciplines. In addition to studying the fundamentals of psychology, human development, and research and statistics methodologies, students enroll in electives that give an overview of the interrelation of psychology and the law.
Students in the forensic psychology track take two specialty courses that provide exposure to several sub-disciplines within psychology and the law, as well as to assessing and managing risk.
Students may also supplement their curriculum with free courses from Palo Alto University's Division of Continuing and Professional Studies, which has a strong legacy of expert-led forensic psychology programs.
Designed for graduate students who want to use technology to improve mental health, this concentration offers a deep understanding of the interplay between psychology and rapidly changing technology. Students analyze the current trends in mental health and wellness, the changing demands of the technology workforce, the expansion of the mental health and technology venture and corporate sector, and how an understanding of psychology can benefit those who want to work in technology.
Through this concentration, graduate students can pursue technology-related careers in fields such as education, nonprofits, government, and more.
Graduates will understand the current trends in mental health and wellness, the changing demands of the technology workforce, the expansion of the mental health and technology venture and corporate sector, and the ways in which an understanding of psychology can benefit those who want to work in technology.
The MS in Psychology program’s general track, students take a wide range of psychology and research classes, establishing the foundation of their graduate education.
Graduate students examine essential topics, including human development throughout the lifespan, social and personality psychology, and biological, cognitive, and affective bases of behavior. Additionally, students dive into the history of psychology, psychopathology and psychodiagnosis, and the ethics of working in clinical psychology.
Because PAU’s general psychology concentration provides students with highly transferable knowledge and skills, they graduate equipped to work in fields such as higher education, business, technology, and teaching or to apply to graduate school.
APPLICATION
Spring 2026 - Priority Deadline - February 15, 2026
Fall 2026 - Apply by July 31, 2026
Applicants for the MS in Psychology program must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. Click here to find out if you're in an approved state.
"Flexible and Welcoming and Also Beneficial to My Path"
“Finding a position that is flexible and welcoming and also beneficial to my path has been great. I was able to get the Child Custody Evaluation Certificate through PAU, which would ordinarily be difficult because you have to be in person for hours or days at a time, but I was able to spread it out over a couple of months.”

Katherine Matheny MS in Psychology student
"Strong Internships Placements and Industry Connections"
“PAU came highly recommended for its strong internship placements and industry connections, which made it an easy choice for me.”

Maggie Tsai
"Small Cohort Where You Have a Great Student to Faculty Ratio"
“The reason I chose PAU is because I found a true sense of belonging here, and there's this focus on a small cohort where you have a great student to faculty ratio. And to me, that was quite important. That's the support I needed. You're made to feel welcome from day one. ”

David Rouxel PhD in Clinical Psychology Student
"Living Up to Their Mission"
“The hope PAU gave me. It has been indescribable, because I didn't think I would be where I am today and, thanks to PAU, like PAU made that happen. So they're definitely living up to their mission.”

Javi Garces BS in Psychology and Social Action Student
"A Sense of Community is One of the Major Assets"
“We have a culture here in the University of support among cohorts and students and even across different cohorts. That is something that also is very helpful. And I think that the university actively stimulates these types of spaces. Having a sense of community is one of the major assets that you get here at PAU.”

Michel Rattner PhD in Clinical Psychology Student
"PAU Saw My Merits as a Professional"
“I think that PAU saw my merits as a professional, that's a big opportunity I will be grateful for all my life.”

Michel Rattner PhD in Clinical Psychology Student
Five Reasons to Make PAU Your Transfer Choice
- Affordable & Accredited — Flexible & Fast
- 80% Graduation Rate (Compared to 60% National Average)
- Transfer Friendly Pathways: Community College
- 50-Year Legacy of Psychology Education and 16-Year Legacy of Online Education
- Psychology Majors with 21st Century Relevance

BS in Psychology
Admissions Requirements
+Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally-accredited institution or the international equivalent. For applicants to the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling Online program, you must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. While no prerequisites are required to apply, we strongly recommend applicants to have related volunteer or work experience in the mental health field.
GRE scores are not required for admissions to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
- The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
- Classes take place Monday-Thursday evenings from 4-6 pm or 6-8 pm or 6-8:50 pm, depending on the cohort.
- All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting
With the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – which means earning your degree in just nine quarters. Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
Online: Distance Learning Format
+Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally-accredited institution or the international equivalent. For applicants to the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling Online program, you must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. While no prerequisites are required to apply, we strongly recommend applicants to have related volunteer or work experience in the mental health field.
GRE scores are not required for admissions to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
- The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
- Classes take place Monday-Thursday evenings from 4-6 pm or 6-8 pm or 6-8:50 pm, depending on the cohort.
- All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting
With the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – which means earning your degree in just nine quarters. Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
MA in Counseling Residencies: Residency Information
+Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally-accredited institution or the international equivalent. For applicants to the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling Online program, you must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. While no prerequisites are required to apply, we strongly recommend applicants to have related volunteer or work experience in the mental health field.
GRE scores are not required for admissions to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
- The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
- Classes take place Monday-Thursday evenings from 4-6 pm or 6-8 pm or 6-8:50 pm, depending on the cohort.
- All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting
With the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – which means earning your degree in just nine quarters. Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
Tuition & Fees
+Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally-accredited institution or the international equivalent. For applicants to the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling Online program, you must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. While no prerequisites are required to apply, we strongly recommend applicants to have related volunteer or work experience in the mental health field.
GRE scores are not required for admissions to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
- The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
- Classes take place Monday-Thursday evenings from 4-6 pm or 6-8 pm or 6-8:50 pm, depending on the cohort.
- All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting
With the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – which means earning your degree in just nine quarters. Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
General Grad Degree Requirements
+Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally-accredited institution or the international equivalent. For applicants to the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling Online program, you must be located in a state in which we are authorized to provide online education. While no prerequisites are required to apply, we strongly recommend applicants to have related volunteer or work experience in the mental health field.
GRE scores are not required for admissions to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
- The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
- Classes take place Monday-Thursday evenings from 4-6 pm or 6-8 pm or 6-8:50 pm, depending on the cohort.
- All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting
With the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – which means earning your degree in just nine quarters. Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.

CACREP Accreditation Fully Accredited Training
Our mix of academic offerings lends itself well to lifelong learners. Bachelor’s, master’s, and doctorate degrees can be complemented with our continuing education programs, all of which strengthen clinical, research, and on-the-job skills.
Cohort Model
PAU’s on-campus format uses a cohort system. You will be assigned to a group of students who will have the same schedule and sequence of courses for their entire program. You will be enrolled continuously and to complete your degree on schedule with their cohort.
Why Cohorts?
Support and openness – you will study together, encouraging and assisting others when needed. You will also develop the familiarity and trust to discuss tough issues and personal experiences.
Cohort Model
PAU’s on-campus format uses a cohort system. You will be assigned to a group of students who will have the same schedule and sequence of courses for their entire program. You will be enrolled continuously and to complete your degree on schedule with their cohort.
Why Cohorts?
Support and openness – you will study together, encouraging and assisting others when needed. You will also develop the familiarity and trust to discuss tough issues and personal experiences.
Cohort Model
PAU’s on-campus format uses a cohort system. You will be assigned to a group of students who will have the same schedule and sequence of courses for their entire program. You will be enrolled continuously and to complete your degree on schedule with their cohort.
Why Cohorts?
Support and openness – you will study together, encouraging and assisting others when needed. You will also develop the familiarity and trust to discuss tough issues and personal experiences.
Cohort Model
PAU’s on-campus format uses a cohort system. You will be assigned to a group of students who will have the same schedule and sequence of courses for their entire program. You will be enrolled continuously and to complete your degree on schedule with their cohort.
Why Cohorts?
Support and openness – you will study together, encouraging and assisting others when needed. You will also develop the familiarity and trust to discuss tough issues and personal experiences.
Online & Hybrid Learning Format
The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
Classes Take Place:
Monday-Thursday Evenings
4-6PM PST or 6-8PM PST or 6-8:50PM PST (Depending on Cohort)
All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting. And with the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – and that means earning your degree in just nine quarters.
Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
The hybrid program is offered weekday evenings. Courses are held on the PAU campuses or live via Zoom.
Classes Take Place:
Monday-Thursday Evenings
4-6PM PST or 6-8PM PST or 6-8:50PM PST (Depending on Cohort)
All skill-based clinical work is done in an appropriate clinical or classroom setting. And with the time savings from your online classes, you will be able to take three classes per quarter – and that means earning your degree in just nine quarters.
Staying local while participating in a distance learning (online) master’s degree program gives students the best of both worlds.
Palo Alto University offers students a multicultural focus that emphasizes culture, social justice, and families that students experience in weekly live classes. Students benefit from the latest academic research and clinical approaches while tailoring their experience to the culture and community in which they live and practice, all in a program format that fits into their busy lives.
How to Apply
PAU's application process is designed with busy students in mind. No letters of recommendation or application fees are required. Students should plan to complete most of their general education requirements prior to enrolling at PAU.
Meet with an Admission Counselor:Learn how your credits will transfer before you apply.
Submit a Transcript Evaluation Today

Admission Requirements
+For consideration for the online master’s in psychology program, applicants must:
- Applicants must hold a bachelor's degree from a regionally accredited institution or the international equivalent. A GPA of 3.3 or higher is recommended. If you have questions about your GPA, reach out to an admissions counselor.
We do a comprehensive review of all your application materials.
Be located in a state in which PAU is authorized to provide online education. - GRE scores are not required for admission to PAU master's degree programs. GRE scores will not be considered in the review of applications, even if students provide them.
- International students may apply for the program if they plan to remain in their home country while enrolled. PAU is unable to enroll students on a student visa into this program.
Applicants typically receive their admissions decision four to six weeks after the interview.
Earn a Terminal Degree
+Students in the Generalist, Tech and Mental Health, and Forensic Psychology concentrations will automatically be awarded the MS in Psychology degree upon successful completion of all graduation requirements.
Students in the PhD Prep Track who successfully complete all academic requirements are awarded the MS in Psychology degree. Those who complete the PhD in Clinical Psychology earn an MS in Clinical Psychology, which supersedes the previously-earned MS in Psychology.Transition to PhD Program
+Students in the PhD Prep Concentration who meet academic qualifications may interview for admission to the PhD program during the summer after their first year.
Those who are offered and accept admission to the PhD program begin PhD studies during the summer quarter after completing their master's coursework.
Admission to the PhD program is selective, and admission is not guaranteed.
Each student must interview with the MS to PhD bridge faculty.
Those continuing to the PhD program, an on-campus program, need to relocate to the Palo Alto area. Students begin PhD coursework during the summer quarter, completing two online courses that are prerequisites for clinical work in the PhD program: Psychometric Theory (4 units) and Introduction to Psychotherapy (3 units).
MS in Psychology students accepted into the PhD program are expected to start their clinical work during the fall quarter of the first year of their PhD program. By that time, they must have completed the two summer courses listed above and also pass the clinical foundations competency exam, which is typically given in late August, and the research competency exam (at either the beginning or end of the summer).
Program Structure & Curriculum
+Convenient evening format: Classes meet online Monday–Thursday between 5–9 pm, with ~90-minute sessions.
The program offers four concentrations, all offered in a synchronous, online format.
- Technology and Mental Health Concentration (6 quarters)
- Generalist Concentration (6 quarters)
- Forensic Psychology Concentration (6 quarters)
- PhD Prep Concentration (7 quarters)
All four concentrations require the same application materials and process.
The MS Psychology program consists of 37.5 or 47 quarter units of coursework, depending on the chosen concentration. There is no thesis requirement. Courses are taken over six or seven consecutive quarters (including summer) beginning only in fall quarter.
|
|
Units |
Quarters |
|
PhD Prep Track |
47 |
7 |
|
Generalist Track |
37.5 |
6 |
|
Forensic Psychology Track |
37.5 |
6 |
|
Tech & Mental Health |
39 |
6 |
Students take two or three courses during most quarters. Students in the PhD Prep Concentration are required to travel to Palo Alto for a one-week intensive course in clinical interviewing.
Sample Schedules
For course descriptions, please see the Palo Alto University Catalog.
General Graduate Degree Requirements
+Quick Application Checklist
How To Apply
PAU uses the psychologyCAS application service. In preparation for applying, you will need a copy of your transcript(s) available for your review. All materials should be submitted through the psychologyCAS system, not directly to the PAU Admissions Office.
- Online Application via psychologyCAS
- Application Fee
- Official Transcripts
- Resume or CV
- Three Letters of Recommendation
- Statement of Purpose
Once Your Application is Complete
Once all application materials have been received and reviewed applicants typically receive an admission decision in 4-6 weeks.
Students accepted into the MS in Psychology program receive an official acceptance letter by e-mail. To enroll in the program, students who have been accepted must submit an enrollment agreement after receiving their acceptance letter to secure their place.
For students who wish to secure financial aid, it is important to begin that process as soon as possible by completing the FAFSA. Once the FAFSA is complete, the PAU Financial Aid office will send the student a PAU financial aid application.
Start Your FAFSA - CODE 021383

Office of Admissions
At Palo Alto University, we’re eager to help you take the next step in your education. You might be advancing your studies, changing direction, or exploring new opportunities—our Admission and Outreach team is ready to guide you with personalized support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Related Program
+Students seeking clinical practice and Marriage and Family Therapist (MST) or Licensed Clinical Counselor (LPCC) credentials should apply to PAU’s MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling, which provides a path to licensure in many other states and countries.
What is the transfer policy?
|
Graduate Level |
Only graduate-level courses are acceptable for transfer credit. A graduate-level course is any course for which a student received graduate credit at their previous institution(s). This may include graduate-level courses the student took as an undergraduate. |
|
Acceptable Grades |
A grade of “B” or better is required in a graduate-level course to be acceptable for transfer credit. |
|
Accreditation |
Previous graduate work must have been completed at a regionally accredited institution. International coursework must be in English in order to be evaluated for transfer. |
|
Time Limit for Requesting Transfer Credit |
Requests for transfer of units must be completed by the posted deadline. |
|
Maximum Units |
A maximum of five units may be transferred into the MS program. If a student receives a waiver of courses beyond the transferable units, they must take elective units to meet the total unit requirement for graduation from PAU. |
|
Units Awarded |
Any course can only transfer in the number of transfer units equal to the comparable course at Palo Alto University, despite the number of units previously assigned to the course. The number of units of a course the student wishes to transfer must be equal to or greater than the units of the corresponding Palo Alto University course. Palo Alto University operates on quarter academic terms. Semester credits will be converted to quarter units for evaluation using a 1.5 quarter unit per 1.0 semester unit conversion. |
|
Course Obsolescence |
Theory (T courses) may be considered for transfer if they have been completed within ten years prior to the time of matriculation at PAU. For all other courses, courses must have been completed within five years prior to the time of matriculation at PAU. |
|
Syllabi |
Students must provide a syllabus/syllabi for the course(s) they would like to transfer. Course descriptions are not acceptable. |
|
Appeals and Exceptions |
Credit transfer decisions may be appealed in writing to the Curriculum Committee. |
Transferable Courses
+| PSYS50 | History & Systems |
| PSYS501 | Child & Adolescent Development |
| PSYS502 | Cognitive Bases of Behavior |
| PSYS504 | Affective Bases of Behavior |
| PSYS505 | Biological Psychology |
| PSYS507 | Adult Development & Aging |
| PSYS509 | Psychopharmacology |
| PSYS511 | Social & Personality Psychology |
| STAT510 | Research Methods & Statistics II |
| STAT511 | Research Methods & Statistics III |
Students may not receive transfer credit for any additional courses, including electives.
Can I complete this program online from anywhere?
+Students can complete the MS from any authorized US state. Please review PAUs list of unauthorized states. If you are located in an unauthorized state, we will not be able to consider your application for admission. If you live outside of the US, you may apply and complete the program from your home country.
How long is the program?
+The PhD prep track is 47 units, and the terminal degree is 37.5 units (one quarter shorter than the PhD prep program).
What are my career options with an MS in Psychology if I do not go on to receive a PhD?
+What's the difference between the MS in Psychology and MA in Counseling?
+The MS is a degree in psychology, while the MA is a degree in counseling. Therefore, the content of classes is quite different. The psychology coursework covers a range of psychology topics, and the year one curriculum is similar to our PhD coursework. Students also receive more exposure to research. The MA courses are specific to counseling and prepare students for a license as a Marriage and Family Therapist (MFT) or Licensed Professional Clinical Counselor (LPCC). Classes cover counseling-specific theories and practice with less emphasis on research methods.
Students who earn the MS do not qualify for any particular license upon graduating, while MA graduates can apply for and work toward a counseling license.
The MS offers a preparatory track to our PhD program, while the MA does not feed into either of our doctoral programs.
Can I see patients or become licensed?
+Can I transfer to the PhD Program?
+The MS in Psychology program was developed specifically to give students an opportunity to demonstrate that they have the ability to handle doctoral-level work at Palo Alto University. The hope is that every student admitted to this program in the PhD Prep Concentration will successfully transition to the PhD program. The Student Progress Committee meets quarterly, approximately two weeks after grades are submitted, to review the progress of all students in the program. Their goal is to identify and provide guidance to any students who may be encountering problems.
Students who wish to continue to the Palo Alto University PhD program will complete a brief application. Interest in and qualifications for the PhD program are discussed with the program director and advisors during the first year of studies. Each student must interview with the MS to PhD bridge faculty.
Qualified MS in Psychology students receive conditional PAU PhD program acceptance letters in the fall of their second year, after completing the MS to PhD interview process. The final offer of acceptance is based on grades earned during the second year of coursework and passing competency exams after completion of all MS in Psychology coursework.
Students must complete all seven quarters of the program, maintaining a minimum GPA of 3.0 with:
- No failing grades
- No more than one B-minus
- No more than one incomplete
Students complete master's coursework by the end of the spring quarter and are then notified when to take their competency exams.
Those continuing to the PhD program, an on-campus program, need to relocate to the Palo Alto area. Students begin PhD coursework during the summer quarter, completing two online courses that are prerequisites for clinical work in the PhD program: Psychometric Theory (4 units) and Introduction to Psychotherapy (3 units).
MS in Psychology students accepted into the PhD program are expected to start their clinical work during the fall quarter of the first year of their PhD program. By that time, they must have completed the two summer courses listed above and also pass the clinical foundations competency exam, which is typically given in late August, and the research competency exam (at either the beginning or end of the summer).
How long is the PhD program?
+What can I do with a Forensic Psychology degree?
+Having an MS in Psychology with an emphasis in forensic psychology affords the same career opportunities as a general MS in Psychology, such as teaching, research, education-related publishing/media, healthcare, and business. However, a forensics emphasis also allows for unique possibilities in the criminal justice system. For example, some correctional facilities in need of psychologists will hire master's-level mental health professionals if they also have a forensics background
What is different about an emphasis on forensics?
+What Courses Will I Take with Technology and Mental Health Concentration?
+PSYS 540 Technology and Mental Health for Children and Adolescents: 1.5 units
With the rise of new technologies our society is being transformed and children and adolescents will be affected both positively and negatively by these technologies. Clinicians working with children and adolescents often advise parents on what to do with their children's technology use (e.g., screen time, cyberbullying, video games, etc). Developing a science-based view of the impact of the new Information and Communication Technologies on the children and adolescents development could help clinicians provide better recommendations for parents.
Additionally, technologies can be specifically designed to treat and prevent mental health disorders in children and adolescents. Even more, Behavioral Intervention Technologies (BITs) may have the capacity to expand delivery models and/or increase the outcomes of therapy. BITs are defined as mobile and electronic interventions that incorporate a variety of technologies, such as mobile phones, the Internet, and virtual reality, in order to assist users in altering behaviors and cognitions related to mental and physical health wellness (Mohr, Schueller, Montague, Burns, Rashidi, 2014).
Emphasis will be placed on treatments designed to be effective with the most commonly occurring pediatric and adolescent health conditions and mental disorders. New professionals trained for the future of mental health care will require to be familiarized with the evidence for and utilization of BITs such as virtual reality, artificial intelligence, Internet interventions, mobile health, wearables, etc.
Course Learning Outcomes
- Understand the attitudes towards technology present in youth, parents and mental health professionals
- Develop a critical view of the impact of the new Information and Communication Technologies on the children and adolescents development.
- Understand the impact that new technologies have on youth development, including recommendations that clinicians can give parents on how to deal with technologies.
Describe the main Behavioral Intervention Technologies (BITs) with empirical support for children and adolescents, including apps, websites, and videogames.
PSYS 541 Evidence-based Digital Interventions to Reduce Health Disparities: 1.5 units
The course will focus on how to blend psychology and technology to help the greatest number of people possible worldwide. Mental Health professionals in the 21st Century will increasingly use digital tools to enhance the effectiveness of their interventions and to expand their reach to serve those currently underserved, including those who do not speak English. These tools have the potential to reduce health disparities and reach diverse populations.
We will examine the growing number of online psychological interventions for health (Websites, mobile applications, and other digital tools) that have been shown to be effective in formal outcome studies. Therefore, the course will be particularly useful to students interested in working in tech and health companies.
Course Learning Outcomes
- Differentiate between the concept of consumable vs. non-consumable interventions
- Identify characteristics of internet evidence-based interventions
- Understand the ethical and legal issues in the practice of psychology, with a focus on the use of technology
- Demonstrate how to evaluate the relevance of published studies for diverse populations
PSYS 542 Principles of Multimedia Learning for Product Design: 1.5 units
Designing effective digital products such as educational videos and interactive educational modules requires an understanding about how people learn. This course introduces students to the Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning (CTML), a theory about how people learn and process information. Students will also be introduced to evidence-based principles that can be used as a framework when designing multimedia content.
We will examine the evidence about the effectiveness of the principles of multimedia learning, design/create two digital products and evaluate existing digital products. The core part of the course will focus on the CTML and principles of multimedia learning, however, there will be a brief introduction to other design frameworks such as Backward Design and ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation). Students will also receive a brief introduction to UX Design.
Course Learning Outcomes
- Demonstrate foundational knowledge of the Cognitive Theory of Multimedia (CTML) Learning and Principles of Multimedia Learning.
- Apply the CTML and Principles of Multimedia Learning as a framework to design two digital educational products, a video and an online interactive module.
- Students will use the CTML and Principles of Multimedia Learning as a framework to evaluate existing educational videos.
- Students will annotate bibliographies based on Principles of Multimedia Learning research publications to further expand their knowledge of these principles.
- Students will demonstrate understanding of additional design theories that they could further explore after the course has ended.
PSYS 543 Mental Health and Design in the Digital World (User Experience): 3 units
This course is designed to introduce students to concepts, considerations, and research at the intersection of mental health and digital product design. It intends to help encourage critical thinking about mental health and design in the digital world, drawing on theories and concepts from clinical psychology, social psychology, and associated disciplines.
It will also provide an introduction to skills and strategies necessary for user-centered design of digital mental health products, including user experience interviews, survey design and qualitative data analysis.
Course Learning Outcomes
- Students will be able to describe different UX/UI approaches, and best practices with respect to design research and implementation strategies.
- Students will create effective UX surveys and interviews to gather quantitative and qualitative data about product design.
- Students will build or enhance skills related to interview and focus group approach, style and pacing.
- Students will apply data analysis techniques specific to design research and evaluation.
Can I transfer credits from the MA to the MS?
+Up to 13.5 units are transferable between the MS and MA, including:
- Psychopathology I
- Psychopathology II
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning I
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning II
- Clinical Interviewing
- Research Methods
- Research and Program Evaluation
Other classes may be reviewed on an individual basis.
Can students from outside the United States participate in the program?
+Do online formats take place entirely online?
+Can this transfer into PsyD?
+Currently, there is no direct transfer from the MS to the PsyD. However, the MS does serve as a preparatory program for our PhD in Clinical Psychology. Interested MS students may apply to the PhD during their first year.
If an MS in Psychology PAU student is admitted to our PhD program, they will enter into year two of the PhD program upon successful completion of their required 47 units.
I am an F-1 International Visa student. Can I apply to Palo Alto University's MA in Counseling or MS in Psychology programs?
+Is this degree accredited by the American Psychological Association?
+What are the Available Student Services
+Faculty Advisors
All students in the MS in Psychology program are assigned an academic advisor upon entry into the program. The primary role of the advisor is to assist with academic planning and to provide guidance on any personal or interpersonal issues that may arise. Because learning online can present unique challenges, academic advisors also serve as online success coaches, checking in with students monthly by phone, email, or both. The first meeting with an advisor is in an online video chat format. PhD Prep Concentration students and advisors meet face to face during the one-week intensive course at the PAU campus in Palo Alto. Throughout the program, students also have quarterly meetings to ensure that all their needs are being addressed. Students are strongly encouraged to be proactive and contact their advisors as soon as they have questions or if any difficulties arise.
At the beginning of the program, all students attend an orientation via web conference to ensure that everyone starts out on the same page with respect to academic expectations, online learning formats, available services, where to turn when needing assistance, etc.
Student Assistant Advisor
A student advisor is available for help, support, and proctoring. The student advisor is a PhD student who has successfully completed the MS in Psychology program online.
Student Feedback
Students are required to submit written evaluations of all courses each quarter. This informs the PAU faculty and administration of our strengths and weaknesses as we strive to deliver the best possible program.
Video Conferencing Orientation and Advising Sessions
A live orientation is available and required before courses start. In addition, the Student Assistant Advisor and the program director schedule quarterly video conferences. Moreover, the program director is available throughout the program for individual academic advising sessions.
Academic Resources and Administrative Support
Whether enrolled in an on-campus or online program, all students are members of the PAU community and have access to the full range of student services, including:
- Research Library
- Office of Student Services
- Office of Financial Aid
- Student Organizations
What should I include in my statement of purpose?
Formatting:
- 2-3 pages
- 1.5 line-spaced
- 12-point font
- 1-inch margins
The paper should include:
A brief autobiographical sketch, including what led to an interest in a psychology graduate program. Details of goals and purpose in applying to Palo Alto University and how this applies to future career goals. Strengths and accomplishments thus far that have prepared the applicant for graduate psychology education.
Personal qualities that will be important assets as a psychologist or in your chosen career field.
What are you looking for in the statement of purpose?
The most important piece of advice is to respond to the questions asked in the prompt and to adhere to length and style requirements. Beyond that, the statement of purpose is the primary way for the Admissions Committee to hear your voice. There is no need to rehash your resume – take the opportunity to talk about your passions and interests specific to psychology.
You are welcome to address personal circumstances or hardship in your application if it helps frame your interest in the field. Please remember, however, that your statement of purpose is not a diary entry or a counseling session.
Oversharing can raise concerns about boundary issues and personal judgment. If you address a past hardship, we encourage you to provide analysis and self-reflection of the situation, rather than just a description of what happened. If the situation is too fresh, and you feel you cannot distance yourself enough to provide analysis yet, it may be best to choose another topic for your statement of purpose.
Didactic Coursework
+With the exception of the summer clinical interviewing course in Palo Alto, the courses are didactic in nature and do not include an applied clinical component. That is why the specific degree associated with the program is an MS in Psychology, not clinical psychology, even though some of the content is relevant to clinical psychology.
The curriculum for this online program is similar to the first year of Palo Alto University's residential PhD program, and many courses are taught by the same faculty members as the on-campus program. This ensures high-quality instruction in both the online and on-campus programs. PAU's institutional data indicate that the performance of students in the online PhD Prep Concentration is comparable to that of students taking the same curriculum on campus.
Students take two or three courses during most quarters. Students in the PhD Prep Concentration are required to travel to Palo Alto for a one-week intensive course in clinical interviewing.
More Available Student Resources
+Canvas
Some portions of each course are completed on the student's own time, at their convenience via Canvas, an educational technology company that hosts courses and course materials in a web-based learning management system. Many classes use PowerPoint slides accompanied by lecture notes. A number of classes include an audio track so students can listen to the instructor. Readings in PDF format and streaming or video downloads for all classes are available through the learning management system.
Interaction at Scheduled Times
Courses also include chat rooms, video conferences or conference calls, which individual instructors schedule at times that work for their enrolled students. Real-time classes typically take place after 4 pm Pacific time on week days.
Assessing Online Coursework
Student performance is assessed in a number of ways, including exams, papers, and project assignments.
Computer and Equipment Requirements
A computer with internet connection is the virtual campus for this program. Students will need access to a reliable computer with an internet connection to participate. A powerful computer with a DSL or cable modem connection is recommended to participate in online classes and download course materials. Students also need a working microphone and speakers to join video and phone discussions.
Online Teaching Methods
Palo Alto University uses a number of methods to accomplish the program's educational goals. Every class includes real-time interaction in a virtual classroom as well as materials that students read and complete on their own. Instructional techniques include:
- Weekly evening remote classes in a virtual Zoom classroom. Instructors share a screen with all students simultaneously and the class members can engage in discussion while viewing the same materials.
- Threaded discussion groups, where students discuss course materials with each other and the instructor.
- Chat rooms or conference calls hosted by the professor that provide a forum for questions and dialog.
- Audio and video conferencing.